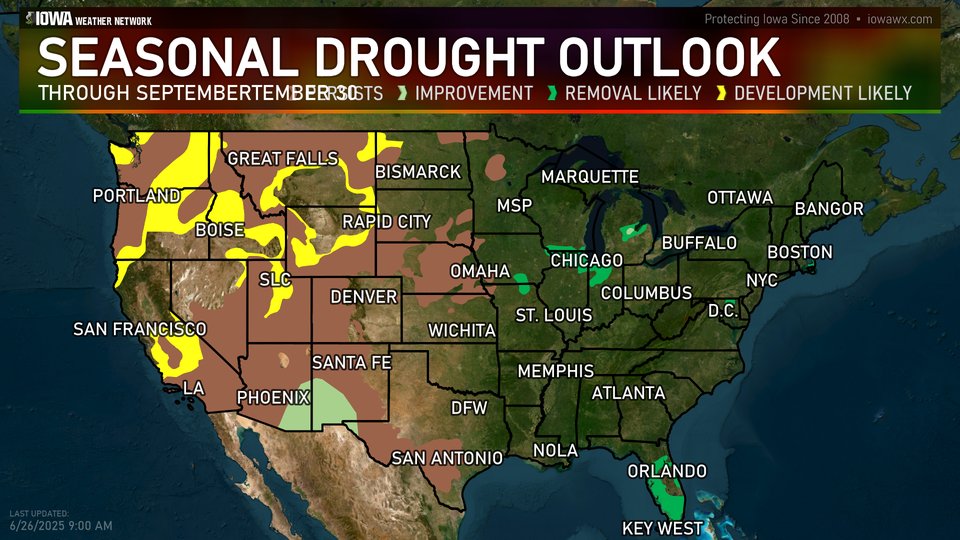
STATISTICS
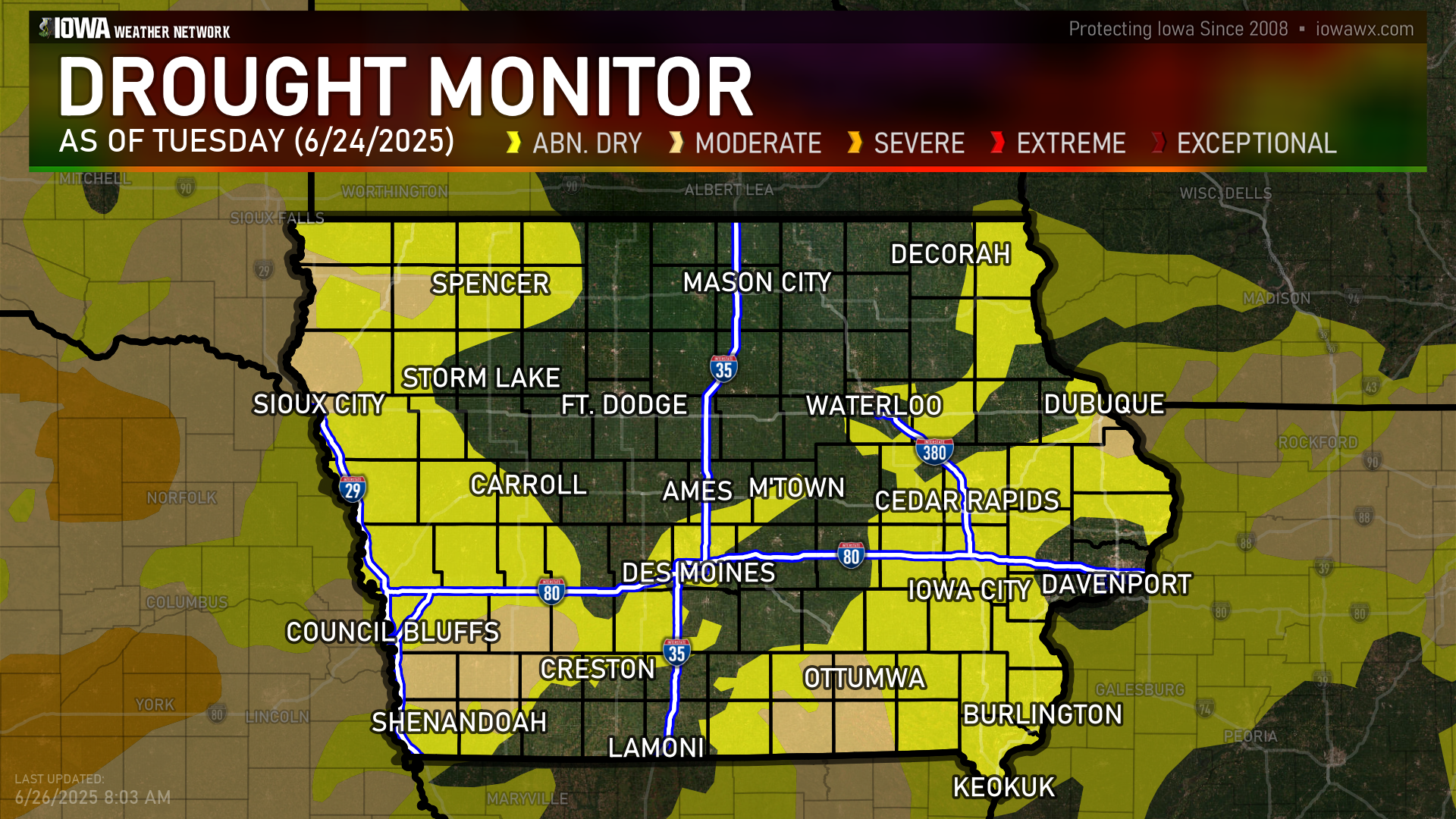
| Week | Date | None | Abnormally Dry | Moderate | Severe | Extreme | Exceptional | DSCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current | 2025-06-17 | 31.47 | 68.53 | 11.63 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 80 |
| Last Week | 2025-06-10 | 20.49 | 79.51 | 12.48 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 92 |
| Three Months Ago | 2025-03-18 | 20.93 | 79.07 | 56.42 | 1.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 137 |
| Start of Calendar Year | 2024-12-31 | 20.16 | 79.84 | 57.33 | 1.30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 138 |
| Start of Water Year | 2024-10-01 | 6.02 | 93.98 | 23.20 | 1.29 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 118 |
| One Year Ago | 2024-06-11 | 83.65 | 16.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 16 |
DISCUSSION
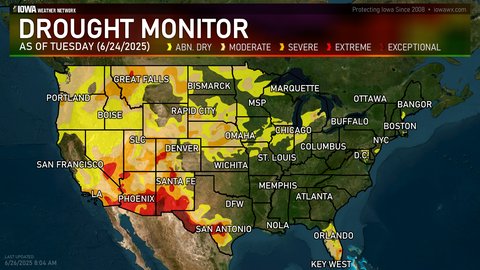
Active weather east of the Rockies led to significant reductions in drought coverage, especially in Florida, Texas, the northern and central Plains, and the upper Midwest. Amid early-summer showers, drought-free conditions largely continued from the southern Plains to the Atlantic Coast, excluding parts of Florida. Meanwhile, a Western hot spell—accompanied by short-term dryness across roughly the northern half of the region—was manifested in rapidly developing soil moisture shortages, declining prospects for summer water supplies, an elevated wildfire threat, a boost in irrigation demands, and increased stress on rain-fed crops.
The NWS 6- to 10-day outlook for June 24-28 calls for the likelihood of above-normal temperatures across much of the eastern half of the country, as well as the northern Rockies and environs, while cooler-than-normal conditions will be mostly limited to the Southwest. Meanwhile, near- or above-normal rainfall can be expected nationwide, with an area stretching from the Southwest into the Great Lakes States having the greatest likelihood of experiencing wet weather.
Forecast
Active weather will shift eastward during the next couple of days, as a hotter, drier pattern envelops the nation’s mid-section and quickly expands. Additional rainfall could total 1 to 3 inches across the eastern one-third of the United States, with some of the highest amounts expected from the lower Great Lakes States into northern New England. However, by the end of the week, any significant precipitation should be limited to parts of the North, with hot, dry weather dominating the remainder of the country. During the weekend, high temperatures should top 100°F in the western Corn Belt as far north as South Dakota, while readings will reach 95°F in nearly all areas of the Midwest. By Sunday, however, cooler air should spread as far east as the northern High Plains. During the transition to cooler weather, showers will develop from the Pacific Northwest to Montana. In the East, the first major heat wave of the season will persist into the first half of next week, with high temperatures near 100°F expected at lower elevations of the Atlantic Coast States from Georgia to southern New England. There are some indications that, by early next week, remnant tropical moisture once associated with Eastern Pacific Hurricane Erick could be entrained by a cold front, leading to an increase in shower activity from the southern Rockies into the upper Midwest.The NWS 6- to 10-day outlook for June 24-28 calls for the likelihood of above-normal temperatures across much of the eastern half of the country, as well as the northern Rockies and environs, while cooler-than-normal conditions will be mostly limited to the Southwest. Meanwhile, near- or above-normal rainfall can be expected nationwide, with an area stretching from the Southwest into the Great Lakes States having the greatest likelihood of experiencing wet weather.